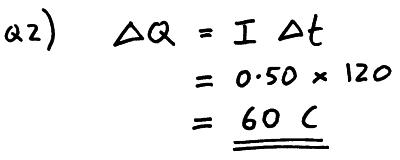Charge Equals Current Times Time
Ise humlog c10 bhi kahte hai.
Charge equals current times time. So the unit for current is a whereas a is c s where c is the unit for charge and s is second for time. You should also learn the formula in the internationally agreed characters. The power p in watts w is equal to the voltage v in volts v times the current i in amps a. A current of 2 a flows for 30 seconds through a lamp.
One coulomb of charge is equivalent to 6 250 000 000 000 000 000 electrons. I t is the momentary current i at time t in amps a. How much charge has moved. V v i a r ω.
Electrical current is the amount of charge that passes across that cross section per unit of time. I t dq t dt. The voltage v in volts v is equal to the current i in amps a times the resistance r in ohms ω. Current in a closed circuit that includes a source of potential difference voltage there will be a current flowing.
Calculate the quantity of charge which has passed through a cross section of the wire during the time t 2 sec to t 6 sec. The current in a wire varies with time according to the equation i 4 2t where i is in ampere and t is in sec. Hours charging time equals to 12 x ahr hrs or 12 1000 x mah hrs 12 1000 x mah hours of charging example calculations with this manual formula. Charge current time.
The amount of charge is the current times the time so after 5hours at 2 amps it has taken a charge of 10 amp hours. Battery ka rating ka 10 isliye lete hai ki mera battery achche se charge ho. What is 2 over 2 minus 1 equals 5 over 6. Therefore i is the current q is the charge and t is time.
This is standard charging and good for battery life. Q t is the momentary electric charge in coulombs c. Calculate charging time length for 2400 mah nimh aa size 1 2v rechargeable batteries with 100 ma charger and secondly with a 3 5 times more powerful 350 ma current output power charger. Electrical current is measured by the rate of electric charge flow in an electrical circuit.
The questions on this page test your ability to use the formula. That is charge per time. Aisa nhi hai ki kam current se charge nhi kr skate jitna kam current se charge karege utna hi battery charge thik hoga but time jayada lagega. The momentary current is given by the derivative of the electric charge by time.
If im not wrong thats the formula for current. Current in an electrical circuit is the amount of charge with respect to time. If the current is constant the last expression you show works. I displaystyle frac q t if the current varies your first expression is appropriate.