State And Explain Ohm S Law In Vector Form

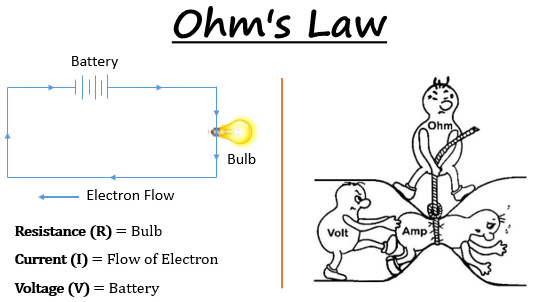
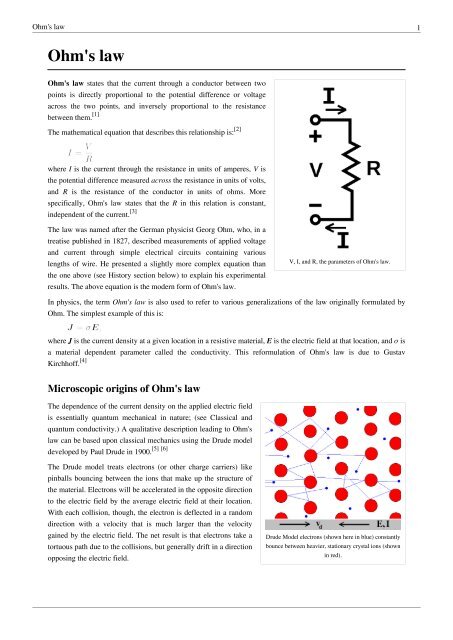
V ir where v is the potential difference i is the current and r is the resistance.
State and explain ohm s law in vector form. Where v is the voltage drop across a resistor of resistance r when a current i flows through it. Introducing the constant of proportionality the resistance one arrives at the usual mathematical equation that describes this relationship. Now current density j is a. Let us generalize this law so that it is expressed in terms of e and j rather than v and i.
The statement implies that the ratio of voltage and current is constant and is called resistance. The vector form is j σe where j the current density si unit. This has been a great help to the users of this community. A m e is electric field with si unit v m σ is the conductivity reciprocal of resistivity.
Simply ohm s law is. Ohm s law state that the current is directly proportional to the voltage across the conductor or resistor. This relationship is known as ohm s law. Two spherical conductors a and b having equal radii and carrying equal charges repel each other with a force f when kept a certain distance apart.
In 1828 georg simon ohm a german physicist derived a relationship between electric current and potential difference. To denote the direction of a vector from position vector r 1 to r 2 and from r 2 to r 1 as. Ohm s law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points. However i will briefly explain the ohm s law in vector form below.
What is ohm s law. A third identical spherical conductor out uncharged is brought in contact with b and removed it is then brought in contact with a and removed. The corresponding vector from q 1 to q 2 is r 21 vector. He published an equation for the force causing the bodies to attract or repel each other which is known as coulomb s law or coulomb s inverse square law.
Where i is the current through the conductor in units of amperes v is the voltage measured across the conductor in. A french physicist charles augustin de coulomb in 1785 coined a tangible relationship in mathematical form between two bodies that have been electrically charged. The above equation is the vector form of coulomb s law. Download conductors and insulators cheat sheet pdf.
Now the force on charge q 2 due to q 1 in vector form is. W k t r ρl a a cross sectional area l length of the conductor v ir therefore v. The new force of repulsion between a and b is. Coulomb s law in vector.
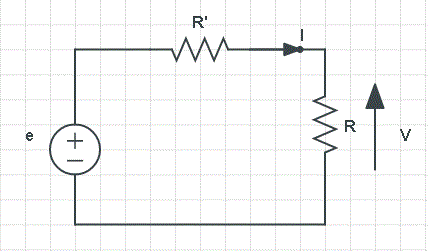
R 21 r 2 r 1. Ohms law definition ohms law application ohms law limitation solving circuits using ohms law ohms law pie chart and matrix table questions. The simplest version of ohm s law. Consider a length l of a conductor of uniform cross sectional area a with a current i flowing down it.
Ohm s law deals with the relationship between current voltage and ideal resistance.