Voltage Drop Across Two Resistors In Series

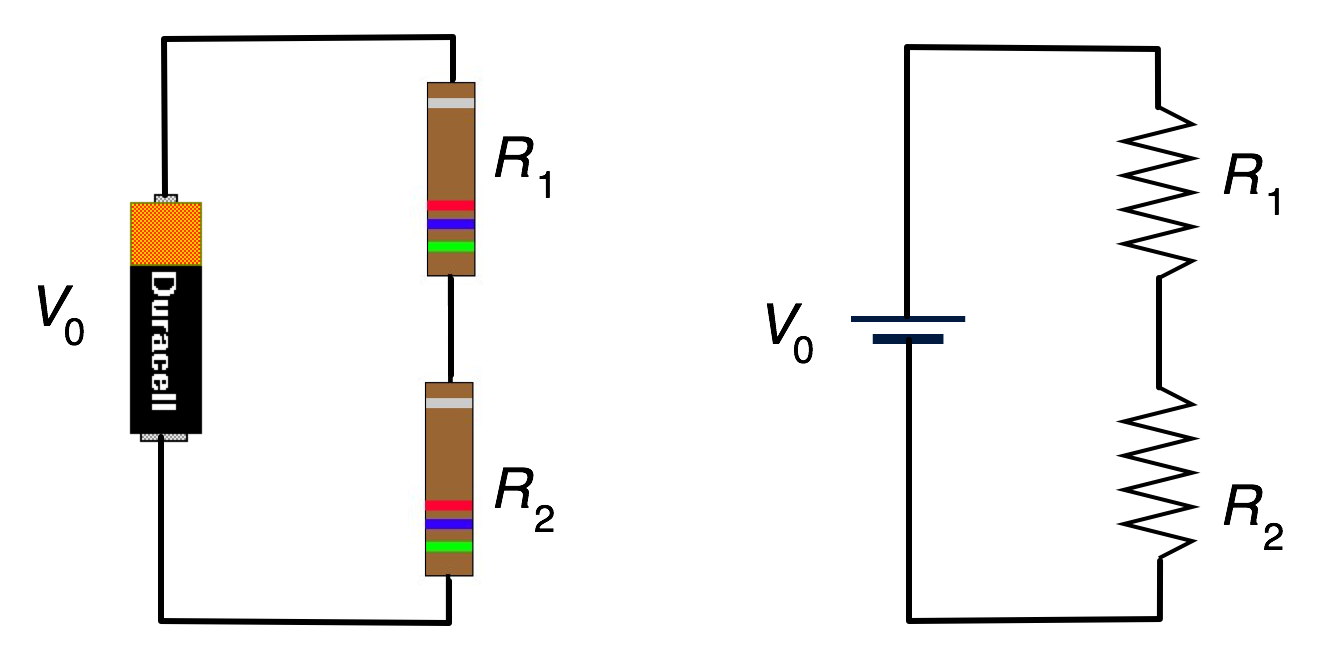
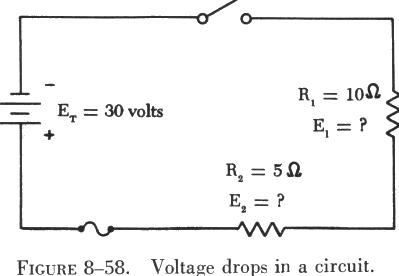
This means that the voltage drop across each is just the total voltage of the circuit divided by the number of resistors in the circuit or 24 v 3 8 v.
Voltage drop across two resistors in series. Resistor voltage drop calculator see the resources for an example of an instance in which you can use an automatic tool to calculate the voltage drop in a kind of circuit arrangement called a voltage divider. Find the circuit current by i e r or i 150 75 2 amps. The total resistance appears as 75 ohms to the 150v source. This is because both the resistors have common potential points shared between them point a point b so the voltage will be the same but the current will be different.
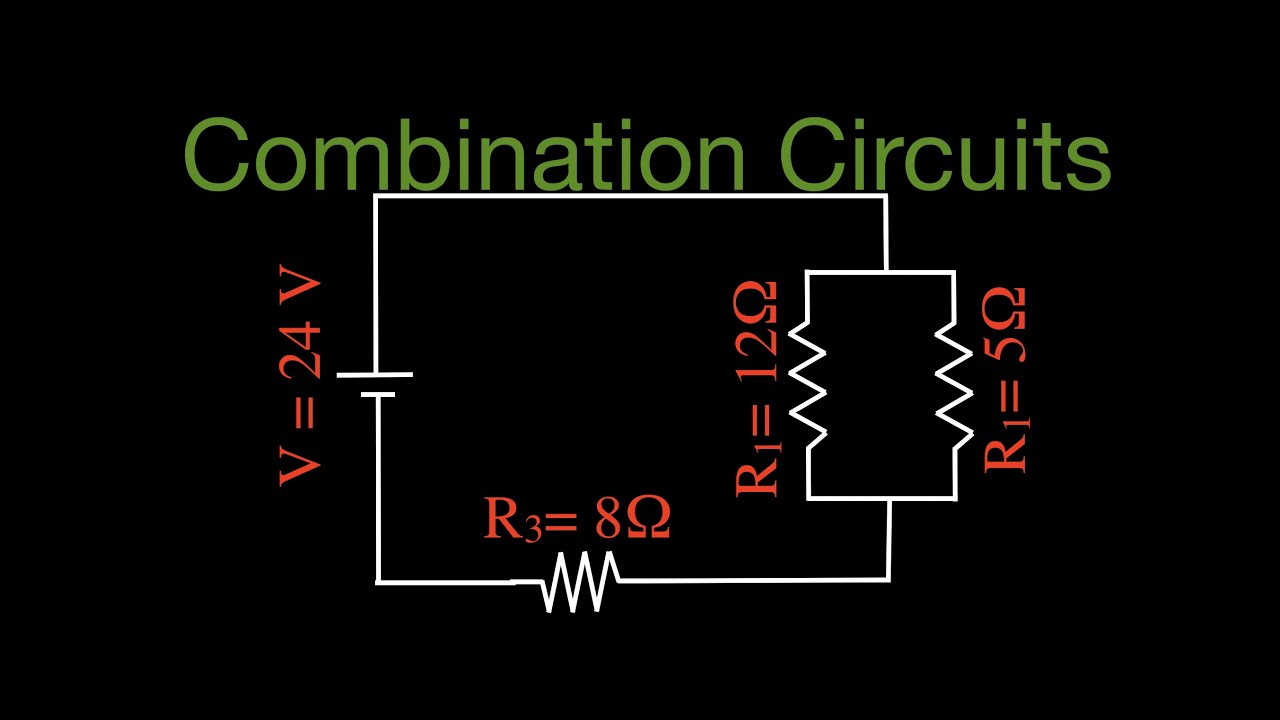
Conversely if you are given two resistors in series with values of 100 ohms and 200 ohms and know that a 12 volt power supply is attached to them you can calculate the current flow through the circuit and how much voltage is dropped by each resistor. The two parallel 30 ohm resistors have an equivalent resistance of 15 ohms. In this circuit the voltage drop across these parallel resistors is the same as that of power supply. Using ohm s law to calculate voltage changes in resistors in series.
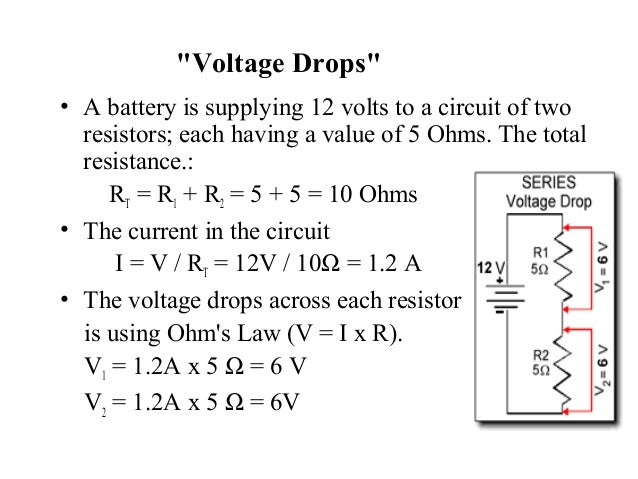
The voltage e 1 across r 1 is therefore. The total voltage applied to the circuit is 110 volts. Since the value of the resistors is known to be 5 ohms each and the current through the resistors is known to be 2 amperes the voltage drops across the resistors can be calculated. Resistors in series carry the same current but the voltage drop across them is not the same as their individual resistance values will create different voltage drops across each resistor as determined by.
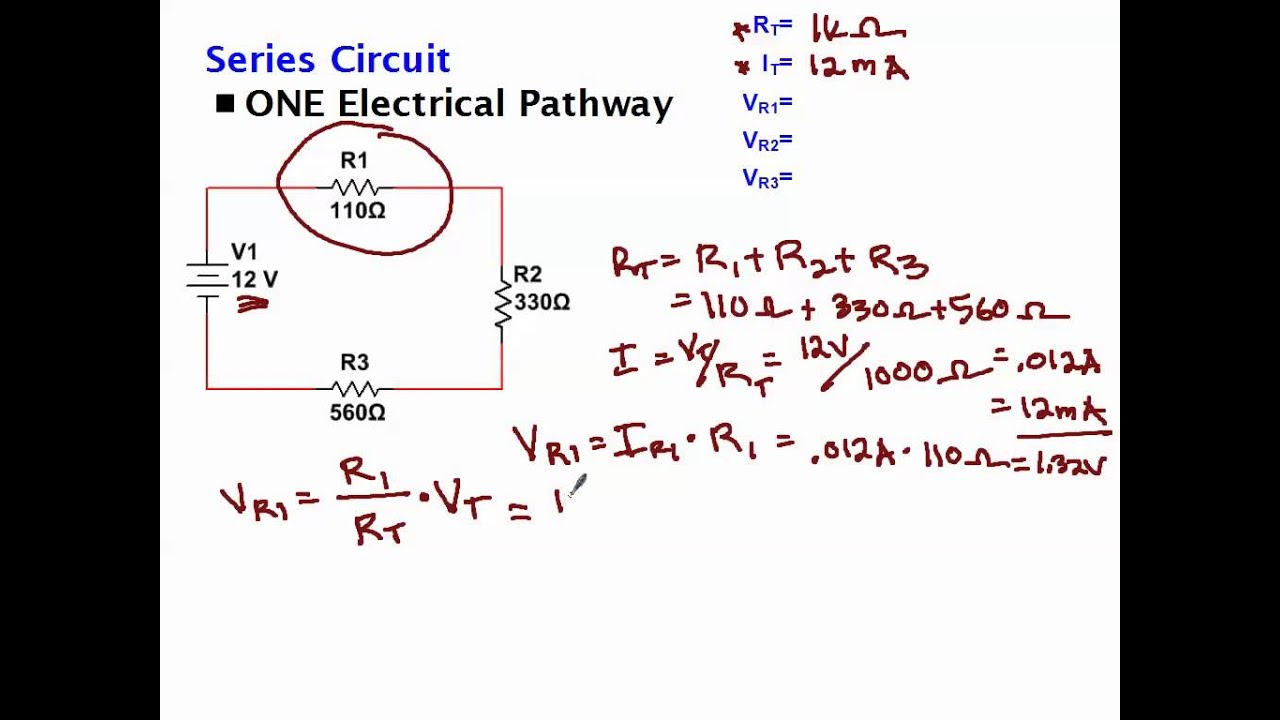
The equation that defines the voltage drop across loads in a series circuit is e i x r. When two or more resistors are connected together end to end in a single branch the resistors are said to be connected together in series. Calculating individual voltage drops in a series circuit. Find the voltage drop for the 60 ohm resistor with e i x r or e 2 x 60 120v drop across the 60 ohm resistor.
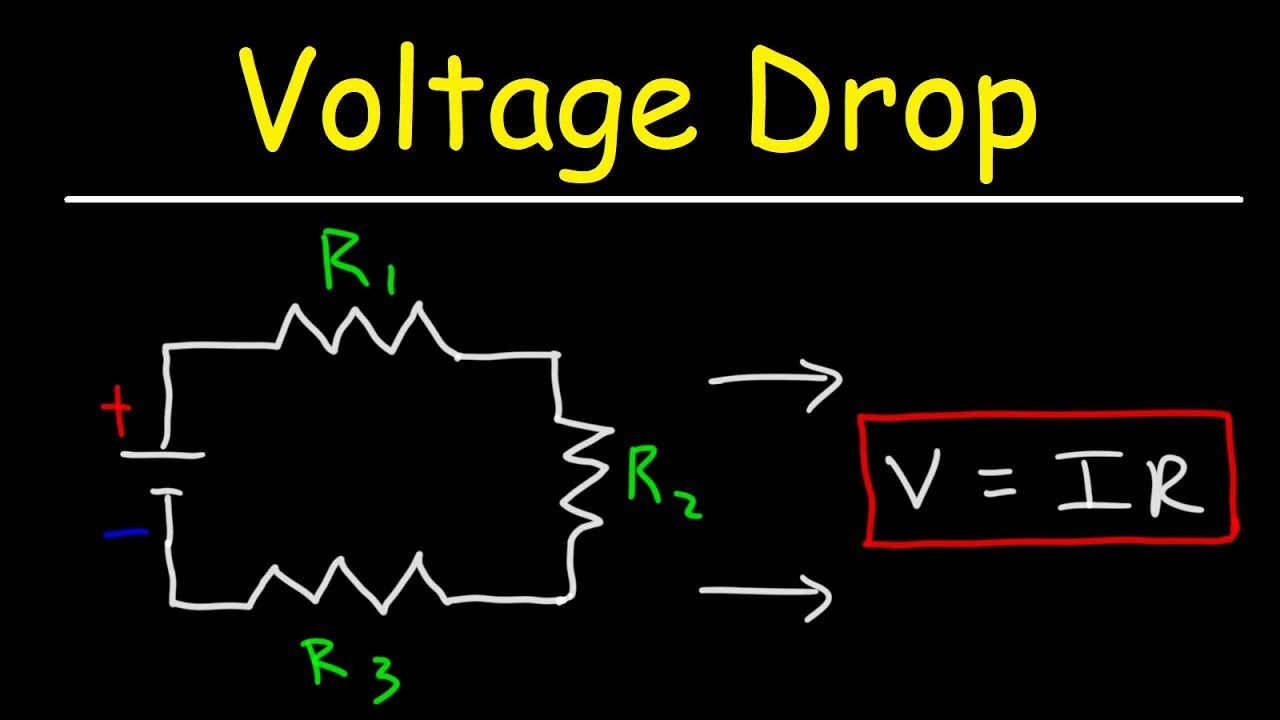
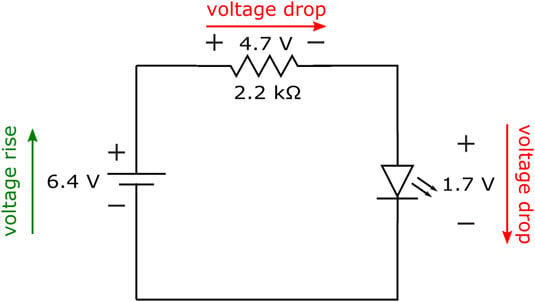
According to ohm s law the voltage drop v across a resistor when a current flows through it is calculated by using the equation v ir where i is current in amps a and r is the resistance in ohms ω.