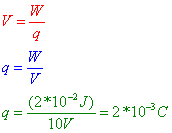Voltage Equals Work Over Charge

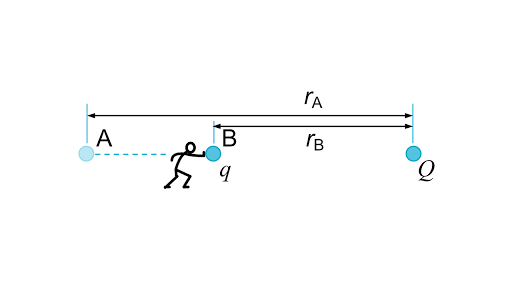
If moving a positive charge from point b to point a requires positive work then point a is said to have a positive voltage with respect to b.
Voltage equals work over charge. The electric field is by definition the force per unit charge so that multiplying the field times the plate separation gives the work per unit charge which is by definition the change in voltage. When a voltage is applied to these plates an electrical current flows charging up one plate with a positive charge with respect to the supply voltage and the other plate with an equal and opposite negative charge. Field from infinite plate part 1 proof. Voltage is a specific measure of potential energy that is always relative between two points.
This difference in charge between the two points is called voltage. Written by willy mcallister. When we speak of a certain amount of voltage being present in a circuit we are referring to the measurement of how much potential energy exists to move charge carriers from one particular point in that circuit to another particular point. We define voltage as the amount of potential energy between two points on a circuit.
In the international system of units the derived unitfor voltage potential difference is named volt. The voltage in volts is equal to the work required in joules divided by the amount of charge in coulombs. Then a capacitor has the ability of being able to store an electrical charge q units in coulombs of electrons. That concept is voltage.
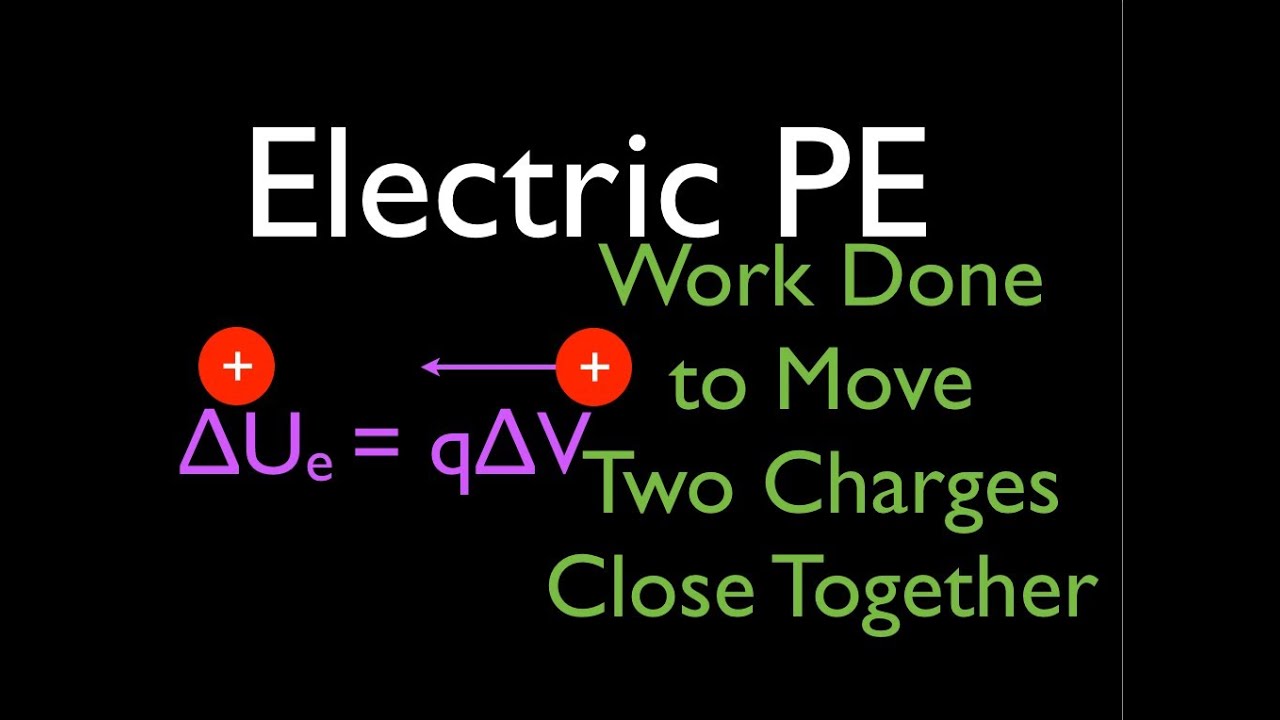
The potential energy is a form of energy and the potential and therefore voltage when differences are taken is defined as the potential energy or potential energy difference per unit charge v e q. If you re seeing this message. The conventional volt v 90 defined in 1987 by the 18th general conference on weights and measures and in use from 1990 is implemented using the josephson effect for exact frequency to voltage conversion combined with the caesium frequency standard for the josephson constant k j 2e h where e is the elementary charge and h is the planck constant a conventional value k j 90 0. One point has more charge than another.
Formal definition of electric potential and voltage. That s equivalent to your equation.